Intent
Provides an abstraction or an interface and lets subclass or implementing classes decide which class or method should be instantiated or called, based on the conditions or parameters given.
Where to use & benefits
- A class wants its subclasses to specify the object.
- The code needs to deal with interface, not implemented classes.
- Hide concrete classes from the client.
- Providing hooks for subclasses is more flexible than creating objects directly.
Structure
Participants
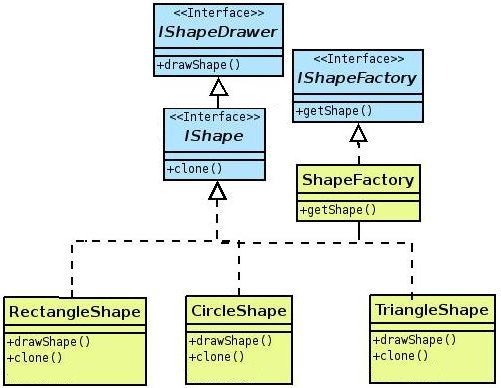
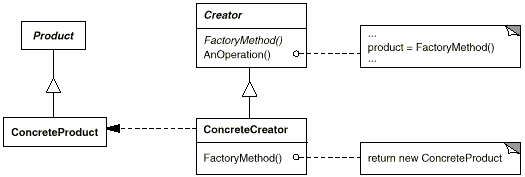
Product (IShape)
It defines the interface of objects which created by factory method.
ConcreteProduct (RectangleShape, CircleShape, TriangleShape)
It implements the Product interface.
Creator (IShapeFactory)
It declares the factory method, which returns an object of type Product.
ConcreteCreator (ShapeFactory)
This overrides the factory method to return an instance of a ConcreteProduct.
Example
In the demonstration application, ShapeFactory class provides the factory method (getShape()) to create the shape (Rectangle, Trinagle, Circle) objects.
Class Diagram